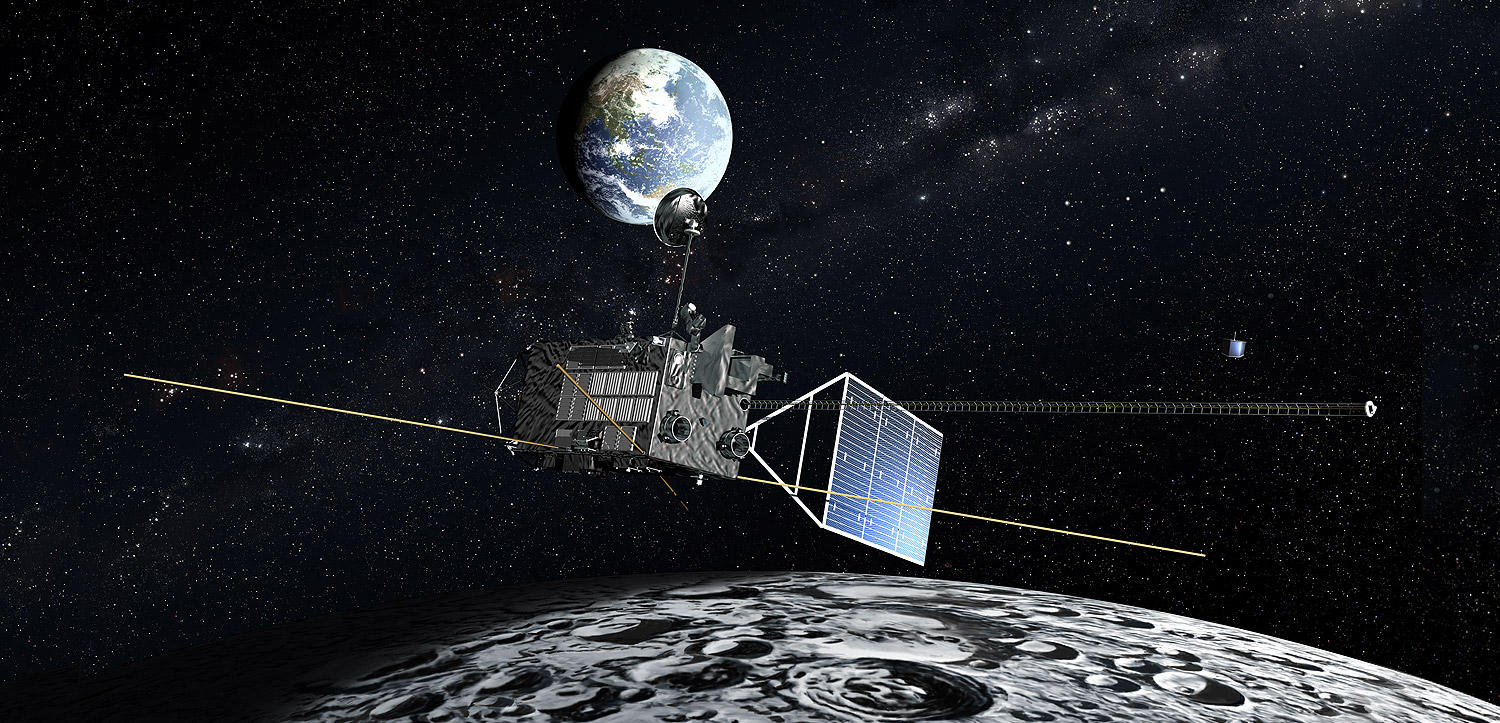
"KAGUYA (SELENE)" was launched by the H-IIA Launch Vehicle at 10:31:01 a.m. on September 14, 2007 (JST) from Tanegashima Space Center (TNSC). The major objectives of the "KAGUYA" mission are to obtain scientific data of the lunar origin and evolution and to develop the technology for the future lunar exploration. "KAGUYA" consists of a main orbiting satellite at about 100km altitude and two small satellites (Relay Satellite and VRAD Satellite) in polar orbit. The orbiters will carry instruments for scientific investigation of the Moon, on the Moon, and from the Moon.
KAGUYA was descended to the 50km altitude from February 1, 2009 and then was descended again to 10-30km in Lower altitude (Perilune) from April 16, 2009. Finally, KAGUYA was impacted to the south-east of near side of the Moon on June 10, 2009 (GMT).
| Name(pre-launch in parentheses) | KAGUYA (SELENE) |
|---|---|
| International Designation Code | 2007-039A |
| Objectives | The major objectives of the KAGUYA (SELENE) mission are to obtain scientific data on lunar origins and evolution, and to develop the technology for future lunar exploration. The scientific data will be also used for exploring the possibility of future utilization of the Moon. |
| Launch Date | September 14, 2007 |
| Launch Location | Tanegashima Space Center |
| Launch Vehicle | H-IIA |
| System Configration | KAGUYA consists of the main orbiter and two sub satellites (Relay satellite and VRAD satellite). |
| Configuration(Main orbite) | 3t, 2.1m x 2.1m x 4.8m |
| Observation Orbit(Main orbite) | Circular orbit, Altitude: 100 km, Inclination: 90° |
| Attitude Control Method(Main orbite) | Three-axis stabilized |
| Configuration(Relay satellite, Rstar) | 50 kg,1 m x 1 m x 0.65 m |
| Orbit(Relay satellite, Rstar) | Elliptical orbit (100 km x 800 km), Inclination: 90° |
| Attitude Control Method(Relay satellite, Rstar) | Spin-stabilized |
| Configuration(VRAD satellite, Vstar) | 50 kg,1 m x 1 m x 0.65 m |
| Orbit(VRAD satellite, Vstar) | Elliptical orbit (100 km x 800 km), Inclination: 90° |
| Attitude Control Method(VRAD satellite, Vstar) | Spin-stabilized |
| Scientific Instruments | 1.X-ray spectrometer (XRS) 2.Gamma-ray spectrometer (GRS) 3.Multiband imager (MI) 4.Spectral profiler (SP) 5.Terrain camera (TC) 6.Lunar radar sounder (LRS) 7.Laser altimeter (LALT) 8.Lunar magnetometer (LMAG) 9.Charged particle spectrometer (CPS) 10.Plasma energy angle and composition experiment (PACE) 11.Radio science (RS) 12.Upper atmosphere and plasma imager (UPI) 13.Four-way doppler measurements by relay satellite and main orbiter transponder (RSAT) 14.Differential VLBI radio source (VRAD) 15.High definition television (HDTV) |
| Reentered Date | June 11, 2009 (Maneuvered falling to the Moon) |