Latest news: For approximately one year, the LiteBIRD team has conducted reformation studies, to make the mission more robust and feasible, without losing its scientific significance. Recently, ISAS/JAXA reviewed the progress, and judged that LiteBIRD can proceed. The international team is accelerating collaborative and unified efforts toward the next step.
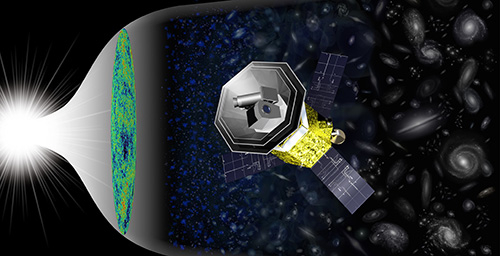
The mission of LiteBIRD is to uncover the origins of the universe and how it began. The Big Bang theory of the universe is now widely accepted after the accumulation of empirical evidence from many prior space and ground-based experiments. But the Big Bang alone cannot fully explain the evolution of the current universe or what happened in the earliest moments of time. The addition of the theory of cosmic inflation, a short period of rapid exponential expansion of space in the early universe, is the prevailing theory that can explain these shortfalls. The LiteBIRD mission aims to find evidence of cosmic inflation through observations of the cosmic microwave background (CMB).
The CMB radiation is remnant light from when the early universe was still a hot plasma. The CMB is very uniform up to approximately one part in 100,000, but these faint variations or anisotropies allow us to accurately probe the earliest state of the universe. Inflation is theorized to create unique primordial gravitational waves that imprint a distinct pattern in the CMB’s polarization signal called the primordial B-modes. These B-modes are “smoking-gun” evidence of cosmic inflation.
The LiteBIRD mission will aim to detect the primordial B-mode signal through developing a CMB spacecraft with a millimeter-wave polarization-sensitive telescope installed. The LiteBIRD spacecraft will observe the entire sky for 3 years at the Sun-Earth Lagrangian point L2 in space. LiteBIRD will achieve unprecedented sensitivities through implementing in total approximately 4,000 transition edge sensor detectors across 12 observational frequency bands and will be capable of distinguishing between the CMB and foreground (dust, synchrotron radiation, etc.) signals. The telescope will be cryogenically cooled to 5 K low temperatures to reduce thermal noise. LiteBIRD will uniformly observe the entire sky with its wide field-of-view and optimized scan strategy utilizing the spacecraft’s spin.
LiteBIRD is a JAXA-led international mission in collaboration with various space agencies and research institutions in Europe (France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom) as well as Canada. The domestic collaborators include the University of Tokyo and Okayama University. LiteBIRD is expected to launch in JFY2032 (JFY: Japanese fiscal year).
2024-10-09 The following was reported to the government’s space science and exploration sub-committee:
In response to KEK’s management decision to relinquish their responsibility for the development of their original technological contribution, the LiteBIRD team will continue investigating reformation plans for approximately one year. After which ISAS/JAXA will judge the continuation of the project.
2025-09-25 The reformation plan was evaluated, and it was concluded that the team should continue and further accelerate the development toward the mission definition review planned in the summer of 2026. The international team will continue collaborative and unified efforts for the reformation studies.
Links
- LiteBIRD Mission Takes One Step Forward (U-Tokyo Kavli IPMU 2025/12/01)
- News release from Canadian Space Agency (CSA) regarding collaboration with Japan and JAXA (July 09, 2025)
- How to capture the universe after its birth through space observation (Okayama University, Research Highlights, January 07, 2025)