| Name (pre-launch in parentheses) | SHINSEI (MS-F2) |
|---|---|
| International Designation code | 1971-080A |
| Objectives | Observation of ionosphere, cosmic rays, shortwave band solar noise, etc. |
| Launch Date | 13:00, September 28, 1971 (JST) |
| Launch Location | Kagoshima Space Center (Uchinoura) |
| Launch Vehicle | M-4S-3 |
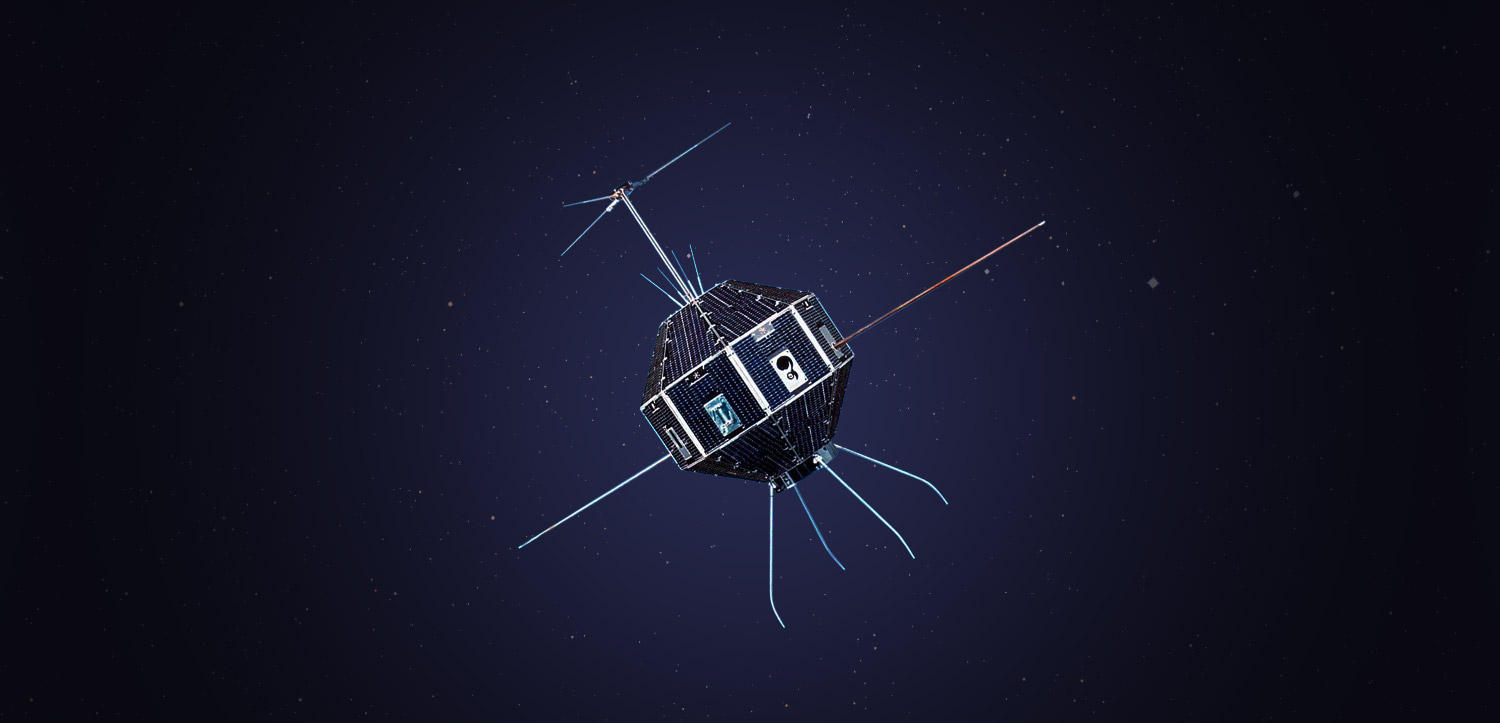
| Weight | 66kg |
| Shape | 26-hedron in a sphere with a 75cm diameter |
| Orbital Altitude | Perigee 870 km, Apogee 1,870 km |
| Orbital Inclination | 32° |
| Type of orbit | Elliptical |
| Orbital Period | 113 min |
| Scientific Instruments | ・Shortwave band solar radio monitor (RN) ・Cosmic ray monitor (CR) ・Ionosphere plasma monitor (ID) ・Geomagnetism attitude system (GAS) ・In-satellite environment monitor (HK) ・Telemetry transmitter (TM-SA) ・Data recorder (DR) ・Command receiver (CM-SA) ・Power supply (PS) ・Satellite timer (MS-SA) ・Nutation damper (ND) |
| End of Operation | June 1973 |
| Operation | After insertion into orbit, Uchinoura received signals to confirm the ionosphere plasma probe deployment, solar-radio antenna extension, and nutation damper operation, and the satellite began operating. The electron-temperature probe was damaged immediately after the satellite was exposed to space and one of the CR's Geiger counters malfunctioned. All other instruments operated normally. |
| Results | Three onboard instruments found abnormal ionization around South America and solar-radio observation revealed the generation mechanism of shortwave-band solar-radio waves. |