TOP > Report & Column > The Forefront of Space Science > 2015 > The X-ray universe that MAXI was watching for five years
![]()

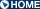
Long-term variation of neutron star binaries MAXI finds the new property how X-ray source fluctuates, which we cannot find out without long observation, as well as a new celestial body and a change of spectral states. Figure 4 indicates the giant outbursts, which Be/X-ray binary (BeXRB) pulsar, A0535+26, caused 4 times succeedingly, arranged in order by the binary orbital period of 111.1 days. We can see that giant outburst occurs by the cycle of 115 days and the orbit phase is shifting to the back gradually. Small brightening (precursor) was also observed by high-sensitivity MAXI, and we found out that it causes by the cycle of 115 days as well. We understood that a node with a pulsar orbit was slipping gradually by Be/Circumstellar disk's precession by 8 year cycle. Depending on X-ray outburst, a strength and a profile of the Hα line are changing, and we elucidate the state of the Be/Circumstellar disk from both sides of an X ray and visible light.
By long observation of the Low Mass X-ray Binary, we found out that there are 2 kinds of ways how the outburst rises and that there are 2 kinds of peak brightness, which corresponds to 2 kinds of instability mode of the accretion disk that was theoretically predicted in 1980's. Flare star Huge flare from a star is one of the unexpected results by an observation of MAXI. Huge flare, which is a million times stronger than that of the sun, was found in the binary star system with the short binary period like RSCVn. We also found huge flare, which is ten thousand times bigger than the sun, in single stars (dMe type stars) which rotate rapidly. These are a thousand times brighter than super flare of G-type star which was recently in the news. The size of the radiation region exceeded that of the star, but the magnetic field was about 50 gausses, which was as much as solar flare (figure 5). It suggests that flare has caused at binary star system and dMe-type star by a same basic mechanism as the sun.
Summary By evaluation of outcomes above-mentioned, the paper of MAXI instrumentation won a prize at Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan (May 2014 issue). Multiwavelength observations of the variable celestial body, such as a supernova and active galactic nucleus, increases the importance, and the role of MAXI, which responsible for the monitoring of the X-ray band, is accordingly prominent. The examination of MAXI, extended until March 2018, is currently performed. Support letters were received from 20 people of 12 countries, MAXI users around the world. In addition to the Swift and "Suzaku" satellite, cooperative observations, which will be performed with ASTRO-H, CALET / GBM, NICER, neutrino telescope, gravitational wave telescope, are planned in the future. As long as the operation of the ISS continues, we want to contribute as an X-ray all-sky monitor of the world even after 2020. (Tatehiro Mihara)
|
||||||||||