TOP > Report & Column > The Forefront of Space Science > 2006 > Next Space VLBI Mission "VSOP-2" by HALCA
![]()

Performance enhancement for VSOP-2 To realize significant improvement compared to the VSOP, three challenging objectives were set for the VSOP-2.
In addition, two important capabilities will be added. In the VLBI observations due to the errors in “phase”, it becomes difficult to achieve high sensitivity or high accuracy. To solve this problem, we plan to introduce a “phase compensation observation” mode where two objects, the targeted source and a reference source located near it, are switched to be observed at an interval of about one minute. This function enables further improvement of sensitivity and astrometry observation. Moreover, by actively conducting polarization observation, we intend to obtain information on magnetic-field direction and Faraday Rotation. These are very important information to understand plasma region, because magnetic field and radiation are closely related. ASTRO-G satellite and technological development One major problem was the design of the ASTRO-G’s radio astronomical antenna. The conclusion we reached was a large deployable antenna (9mø, 0.4mm rms) of the module-structured, offset-parabola type, which differs from that of HALCA. A one-wing solar paddle will be mounted on the opposite side of the antenna. The satellite will adopt three-axis attitude control. Its weight will be about 910kg and generation power about 1.8kW (Fig. 2). 
The observation orbit is planned to be elliptical with parameters of apogee height 25,000km, perigee height 1,000km, orbital inclination 31 deg., and orbital period 6.5 hours. We decided to introduce the LDR (Large-scale Deployable Reflector) structure, which is adopted for the ETS-III satellite, as the large antenna’s deployable structure. The antenna will comprise seven antenna modules. In order to improve mirror surface accuracy of individual modules, newly developed radial ribs will be employed, with a concept identical to the umbrella. A two-axis adjustment mechanism will be installed on its main mirror and three-axis adjusting mechanism on its sub mirror so that we can adjust to keep antenna gain maximum in orbit. Since FY2000, the development budget for the satellite had been allocated in the name of strategic developmental budget prior to its formal selection. We are confident that the deployable antenna will be successfully developed as a result of our intensive study over the past six years including prototype module fabrication (Fig. 3). 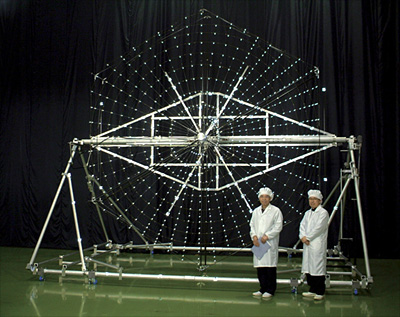
|
||||||||||