TOP > Report & Column > The Forefront of Space Science > 2014 > The Realization of Observing the Gamma-Ray Polarization and Studies on the Radiation Mechanism of Gamma-Ray Bursts
![]()

Revealing the Internal Structure of the Jet From the observation of GAP, let us predict the internal environment of the relativistic jet. First of all, since the gamma ray radiation shows a high degree of polarization, we naturally consider the radiation mechanism should be the synchrotron radiation. The problem is how to deal with the fact that the polarization angle is changing during the burst. In one of the theoretical models for the formation of the relativistic jet, one considered to be spiral and toroidal magnetic fields (Figure 3). Since plasma cannot dissipate freely because of interaction with the magnetic field, it is convenient to narrowly collimate the relativistic jet. When we observe it in front of the jet, we expect the magnetic field to be like a concentric circle. If the emission areas are small patch-like shape, and the direction of the magnetic field inside the patches differs from each patch, the fact that the direction of polarization differs for every pulse of GRB prompt emission can be explained. In small emission areas, the magnetic field is locally coherent (well ordered), so the high degree of polarization as well as changes in polarization angles can be explained. From the observation by GAP, we can investigate some internal structures inside the relativistic jet and also reveal the specific shape of the magnetic fields. This will give important suggestions for the formation of the relativistic jet, one of the big problems in the high-energy astronomy. 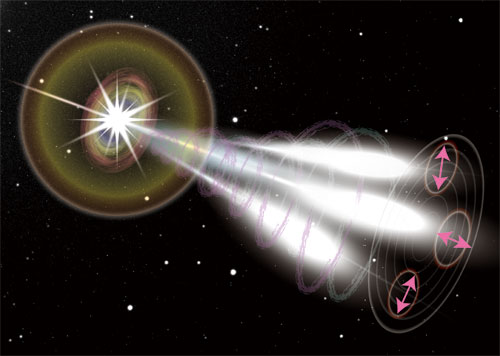
We have introduced that polarization would also be seen when electromagnetic waves are scattered. Actually, there are some theoretical model of GRBs considering such situation. In these observations by GAP, we cannot completely reject the scattering model because of poor statistical accuracy. However, the synchrotron radiation model is being declared the winner for the existence of high polarization degree. As an independent experiment for GRB polarization observation, TSUBAME satellite, developed mainly by Tokyo Institute of Technology and ISAS, was launched in 2014. There are also plans such as the PolariS project in Japan and several X-ray polarization projects proposed to NASA. We are celebrating the dawn of full-scale polarization observations. ASTRO-H would also be able to perform the polarization observations with high accuracy for extremely bright targets. Polarization observation is expected to progress as one of the new fields in high-energy astronomy. In Conclusion We received the 6th Space Science Encouragement Prize and Hokkoku Culture Prize together with Prof. Toshio Murakami for the results from the experiments and observations in our study. Furthermore, Toma Kenji, who did theoretical investigation with us in our study, has been awarded both the Young Scientist Award from the Physical Society of Japan and the Research Award from the Astronomical Society of Japan. We feel that our small experimental project has been given high regards. We have the good fortune to have the chance to install our instruments onboard IKAROS. And it was a good experience to do research with teachers in engineering division. At last, I would like to show my thanks from my bottom of my heart to the GAP team formed by Prof. Toshio Murakami (Kanazawa University), Prof. Shunichi Gunji (Yamagata University), Tatehiro Mihara (RIKEN) and CLEAR-PULSE Co., Ltd., as well as members and manufacturers of IKAROS, who gave great attention to GAP while being busy with the IKAROS project. (Daisuke Yonetoku)
|
||||||