TOP > Report & Column > The Forefront of Space Science > 2014 > Examination of the exploration using the Epsilon rocket
![]()

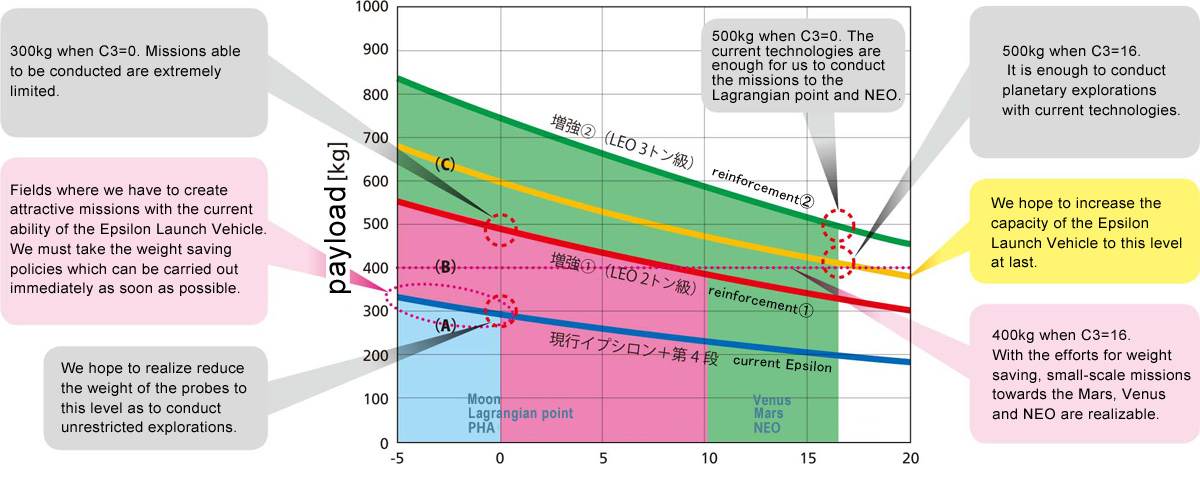
The performance request to Epsilon Thus, by the Epsilon and Scientific Satellite side, required/ realizable ability, and launch frequency are examined mutually. Here, we introduce first this examination work done by the Scientific Satellite (ISAS) side at the end of the 2013 fiscal year. The Japanese space probe stuffed as much apparatus as possible by few chances, and has performed missions at least until now. Therefore, when we estimate the space probe by the old way, the launch capability will be necessary equal M-V rocket. On the other hand, if we ask Epsilon too much request, cost may become higher than H-IIA or its succeeding rocket, and even if it not the case, reinforcement may not be accepted because cost effectiveness is bad. But instead of it, Epsilon has the characteristic that the frequency of about one rocket can respond reasonable in half a year. Then, ISAS side changed the view, and we have discerned the minimum conditions which cannot be yielded in order to function as the space probe, and decided to estimate required capability by the premise of performing compact missions by high frequency compared with the former. If we build space probe with the present technology, mass including observational equipment will be about 500-600 kg, but in fact, this technology is as essentially as ten-year before the same, and has also stuffed a lot of observational equipment. The miniaturization of electronic circuit mounting and the progress in material which still continue were taken in as much as possible, we should divide observational equipment into two or more bodies, and make it the minimum number. And we have decided target weight as 400 kg. 20 to 30 percent of weight saving is very difficult in the space field, if the electronic device which is the essence of exploration equipment becomes light, the structural system holding it will be lighter-weight. The mass of propulsion system which carries them may be able to save weight more. We will aim this amount of reduction on the whole as those results. It becomes another focus of demand how far the space probe which saved weight is launched. If we say the destination of exploration roughly, it is the solar system whole region, but in order to go in the distance from a certain fixed distance, near the planet and satellite where gravitation is powerful, it should conduct swing-by. However, since swing-by usually takes long time compared with direct cruise, if we need to explore in realistic time, it is necessary the capability to arrive directly to the nearby planet of the earth. If we can launch to Mars or Venus, it can further progress using swing-by after that. On the other hand, in order for the approach to the reverse side of the moon and to conduct efficiently the sample return to the asteroid which has strong point by realization of "Hayabusa" in Japan, It is good to make space probe once stagnate an earth = moon Lagrangian point (EML) and near the sun = earth Lagrangian point (SEL), and to launch to an interplanetary space to suitable timing. In this case, since rocket propellant is necessary for going to the destination from staying area and it becomes advanced missions in navigation for various invest in Lagrangian point, it is desirable for there to be mass of about 600 kg. In this way, as required capability reinforcement to Epsilon for a while, we have assumed that it can launch about 400kg space probe is into the revolution orbit of Mars or Venus, or it can launch about 600kg space probe into SEL." And we will consider on the space probe side. Refer to Fig. 1 for the ability of the form of Epsilon under various examinations to launch which space probe into which orbit.
|
||||||